How to Select the Perfect Diamond
 Where Should You Shop for a Diamond?
Where Should You Shop for a Diamond?
Today diamonds are often purchased online, usually with the impression that the price will be lower. But we believe that you should shop for your diamond in person, not online.
Here’s why you should buy your diamond in person:
- Most jewelry stores, including New England Jewelry, have very similar diamond prices to online options
- You’ll work directly with an experienced diamond professional. Most online personnel have no gemological training and don’t even see the diamonds they are selling
- Diamonds are best evaluated by comparing them side by side. Every diamond is unique, and even with the same grading, they will not appear exactly alike!
- You will be able to compare diamonds under magnification, with laboratory equipment and correct lighting
- Reduce your risk of fraud
Please come in and meet us and begin a new friendship with the folks at New England Jewelry.
Finding the Right Diamond – The 4 C’s
 There are 4 major factors to consider when buying a diamond: Carat weight, Cut, Clarity, and Color. When assessing the true value of a diamond, all 4 factors are should be considered collectively.
There are 4 major factors to consider when buying a diamond: Carat weight, Cut, Clarity, and Color. When assessing the true value of a diamond, all 4 factors are should be considered collectively.
Carat
A diamond’s weight is measured in carats, where one carat equals 100 points. So 50 points equals ½ carat and 75 points equals ¾ carat. When a diamond weighs over a carat, the weight is expressed in carats and decimals, rounded to the nearest hundredth of a point (i.e. 1.52 ct).
 A diamond’s carat is a measurement of weight, not size. For example, a perfectly cut one carat round diamond will look bigger than a deeply cut one. Likewise, this same diamond will appear smaller than a wide and shallow cut one.
A diamond’s carat is a measurement of weight, not size. For example, a perfectly cut one carat round diamond will look bigger than a deeply cut one. Likewise, this same diamond will appear smaller than a wide and shallow cut one.
Learn more...
As the diamond carat size increases, the price increases at a faster rate. This is because larger diamonds are much more rare and therefore more valuable. For example, we know that all 4 C’s being equal, larger stones are worth more than smaller ones. However, many people don’t realize that a 2.00 carat diamond is worth more than just twice as much as a 1.00 carat diamond. The diamond value will also change with each incremental change in size, color, clarity and cut quality. Even the shape of the diamond will affect the price!
The size you choose should be based on your preference and your budget. Do as much or as little research as you like. Then come in to New England Jewelry. We’ll show you diamonds side by side, in a comfortable setting, and answer any questions you have. We’re diamond experts and we’d love to help!
Clarity
Nature has ensured that each diamond is as unique as the person who wears it. Naturally occurring “inclusions” such as minerals or fractures are identifying characteristics created when diamonds are formed in the earth. They look like tiny crystals, clouds, feathers or cracks. Clarity measures these inclusions using 10X magnification. The diamond grader examines the clarity characteristics with respect to the nature and number of characteristics, as well as their size, color and position. The clarity grade assigned reflects the degree of visibility of the characteristics.
Of the Four C’s, Clarity has the least impact on a diamond’s appearance, apart from the lowest clarity grades. Larger inclusions will lessen a diamond’s sparkle by limiting the passage of light, thereby lowering its value. In higher clarity diamonds, these imperfections are microscopic and do not affect a diamond’s beauty.
Learn more...
When selecting a diamond, it is always best to view diamonds side by side, unmounted, in optimal lighting. In this controlled environment, if you can’t see any inclusions with the unaided eye, the diamond is considered “eye-clean.” Many SI diamonds are eye-clean and are therefore an excellent value.
For larger diamonds or people with a keen eye for detail, you may want to choose a VS or even a VVS diamond. Without a microscope, you will not be able to discern the difference between these diamonds and the FL or IF diamonds, which command higher prices.
The GIA Diamond Clarity Grade scale has five main categories of clarity characteristics with 11 grades in all.
| GIA Diamond Clarity Grade Scale | |
| FL, IF | Flawless, Internally Flawless: No internal or external imperfections. Internally Flawless: No internal imperfections. Very rare. |
| VVS1, VVS2 | Very, Very Slightly Included: Very difficult to see imperfections under 10x magnification. An excellent quality diamond. |
| VS1, VS2 | Very Slightly Included: Imperfections are not typically visible to the unaided eye. Less expensive than the VVS1 or VVS2 grades. |
| SI1, SI2 | Slightly Included: Imperfections are visible under 10x magnification, and may be visible to the naked eye, especailly in larger SI2 diamonds. An excellent diamond value. |
| I1, I2, I3 | Included: Except for smaller I1 diamonds, inclusions visible to the naked eye. Carefully selected I1 diamonds are a good choice for a limited budget. |
Color
Choosing the right color for your diamond is based on personal preference, but you are generally searching for a stone with little to no color.
 The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) uses a 12-letter alphabetical scale of D to Z to objectively measure diamond color. Using this scale, the diamond on the lower end of the scale (D) will have the least amount of color – it is considered a colorless stone. The diamond at the higher end of the scale (Z) has deeper tones.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) uses a 12-letter alphabetical scale of D to Z to objectively measure diamond color. Using this scale, the diamond on the lower end of the scale (D) will have the least amount of color – it is considered a colorless stone. The diamond at the higher end of the scale (Z) has deeper tones.
Learn more...
However, when a diamond’s color is more intense than the “Z” grading, it enters the realm of a “Fancy Color” diamond. In this case, the intensity of the color in the diamond can play a significant role in its value. The value of a Fancy Colored Diamond can surpass that of colorless diamonds if the intensity of the color is high and the color is rare.
Diamonds graded D through H are generally preferred for white gold or platinum jewelry. Colors below H have a slightly yellowish hue and when selected, are often better suited to yellow gold settings.
Cut
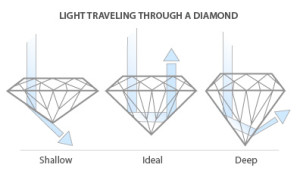 The term “Cut” is often confused with a diamond’s Shape which is the outward appearance of the diamond, such as round, princess, oval or marquis. The Cut of a diamond refers to its proportions, symmetry and finish. Diamonds are given cut grades by the GIA and AGS laboratories.
The term “Cut” is often confused with a diamond’s Shape which is the outward appearance of the diamond, such as round, princess, oval or marquis. The Cut of a diamond refers to its proportions, symmetry and finish. Diamonds are given cut grades by the GIA and AGS laboratories.
The proportions are the size and angle relationships between the facets and different parts of the stone. Finish includes polish and details of facet shape and placement. When the proportion, symmetry, and finish of a diamond are good, you will notice that the diamond is brilliant, sparkly, and full of ‘fire’ or scintillation.
Learn more...
The cut of a diamond is considered to be the most important factor with respect to its beauty. The cut determines the brilliance of the diamonds – how light is reflected , dispersed and scintillated. When a diamond is cut with the proper proportions, light is returned back to us from the top of the diamond. When a diamond is cut too shallow, light leaks out of the bottom; too deep and it escapes out of the side.
Unlike color and clarity, there is not a single grade that defines it. Furthermore, two diamonds equal in carat weight, color and clarity can differ in appearance and value because of differences in cut quality.
New England Jewelry recommends selecting the highest cut grade that fits within your budget. While there are several cut grades, a “Very Good” (GIA) or “Excellent” (AGS) cut grade will sparkle beautifully, although you may notice an improvement in brilliance by upgrading to the best cut grade of “Excellent” (GIA) or “Ideal” (AGS). Only about the top 3% of diamonds are cut to this top cut grade.
GIA, AGS and EGL Certificates
What is a GIA, AGS, or EGL Diamond Report or Certificate?
A diamond certificate or report is created by a team of gemologists who evaluate and measure a diamond. The report contains the diamond’s dimensions, clarity, color, polish, symmetry, and other characteristics. Many round diamonds will also include a cut grade on the report.
Learn more...
What is the difference between GIA, AGS and EGL diamond certificates?
The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) and the AGS (American Gem Society Laboratories) , both nonprofits, are the most respected laboratories in the diamond industry. These laboratories are consistent and conservative in their grading and therefore highly regarded. Both GIA and AGS grade a diamond based on how well it’s cut for three factors: polish, symmetry and cut. The GIA’s highest possible grade is “triple X,” while the AGS’s highest possible grade is “triple 0” (given for excellence in polish, symmetry and cut).
Unlike the GIA and AGS, the EGL (European Gemological Laboratory) is a for-profit organization. Possibly by coincidence, the EGL usually grades diamonds higher than the GIA and the AGS. Therefore, diamonds graded by EGL are not as well respected for accuracy and usually sell at very substantial discounts.
No matter what your budget is for an engagement ring, you want to be treated fairly. Diamonds are our expertise and we’re here to help you make an educated, confident choice!

